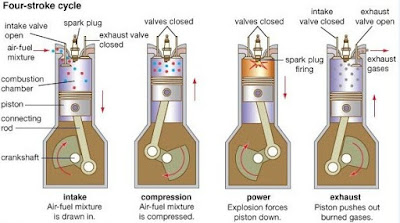
Sequence of Operations in IC Engine
Each
stroke in IC(internal combustion) engines forms a sequence of operations in one
cycle of IC Engines.
These are the name of four strokes.
Ø Suction stroke
Ø Compression stroke
Ø Expansion stroke
Ø Exhaust stroke
Strictly
speaking, when an engine is working continuously, we may consider a cycle
starting from any stroke. We know that when the engine returns back to the
stroke where it started, we say that one cycle has completed. The following
sequence of operation in a cycle is widely used.
1. Suction stroke
In this
stroke, the fuel vapor in correct proportion is supplied to the engine
cylinder.
2. Compression stroke
In this
stroke, the fuel vapor is compressed in the engine cylinder.
3. Expansion or working stroke
In this
stroke, the fuel vapor is fired just before the compression is complete. It
results in the sudden rise of pressure, due to expansion of the combustion
products in the engine cylinder. This sudden rise of pressure pushes the piston
with a great force and rotates the crankshaft. The crankshaft, in turn, drives
the machine connected to it.
4. Exhaust stroke
In this stroke, the burnt gases (or combustion products) are exhausted from the engine cylinder, so as to make space available for the fresh fuel vapor.







Comments
Post a Comment