Valve Timing Diagram of Petrol Engine

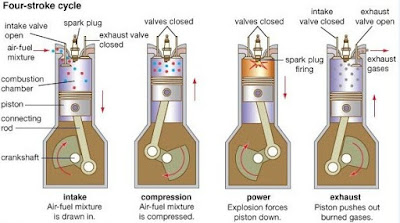
Valve Timing Diagram for a Four Stroke Cycle Petrol Engine -The petrol engines is also known as spark ignition engines.The valve timing diagram for a four stroke cycle petrol engine is shown in Figure: The following particulars are important for a four stroke cycle petrol engine regarding valve timing diagram: (a) The inlet valve opens (IVO) at 10 °- 20 ° before top dead center (TDC) and closes 30 ° - 40 ° after bottom dead center (BDC). (b) The compression of charge starts at 30 ° - 40 ° after BDC and ends at 20 ° - 30 ° before TDC. (c) The ignition (IGN) of charge takes place at 20 ° - 30 ° before TDC. (d) The expansion starts at 20 ° - 30 ° before TDC and ends at 30 ° - 50 ° before BDC. (e) The exhaust valve opens (EVO) at 30 ° - 50 ° before BDC and closes at 10 ° - 15 ° after TDC. Note:- (i) The inlet valve of a four stroke I.C. engine remains open for 230 °. (ii)